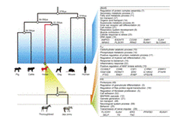
In this study, protein domains with cellulase activity in goat rumen microbes were investigated using metagenomic and bioinformatic analyses. After the complete genome of goat rumen microbes was obtained using a shotgun sequencing method, 217, 892, 109 pair reads were filtered, including only those with 70% identity, 100-bp matches, and thresholds below E−10 using METAIDBA. These filtered contigs were assembled and annotated using blastN against the NCBI nucleotide database. As a result, a microbial community structure with 1431 species was analyzed, among which Prevotella ruminicola 23 bacteria and Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus B316 were the dominant groups. In parallel, 201 sequences related with cellulase activities (EC.3.2.1.4) were obtained through blast searches using the enzyme.dat file provided by the NCBI database. After translating the nucleotide sequence into a protein sequence using Interproscan, 28 protein domains with cellulase activity were identified using the HMMER package with threshold E values below 10−5. Cellulase activity protein domain profiling showed that the major protein domains such as lipase GDSL, cellulase, and Glyco hydro 10 were present in bacterial species with strong cellulase activities. Furthermore, correlation plots clearly displayed the strong positive correlation between some protein domain groups, which was indicative of microbial adaption in the goat rumen based on feeding habits. This is the first metagenomic analysis of cellulase activity protein domains using bioinformatics from the goat rumen.
In this study, protein domains with cellulase activity in goat rumen microbes were investigated using metagenomic and bioinformatic analyses. After the complete genome of goat rumen microbes was obtained using a shotgun sequencing method, 217, 892, 109 pair reads were filtered, including only those with 70% identity, 100-bp matches, and thresholds below E...
In this study, protein domains with cellulase activity in goat rumen microbes were investigated using metagenomic and bioinformatic analyses. After the complete genome of goat rumen microbes was obtained using a shotgun sequencing method, 217, 892, 109 pair reads were filtered, including only those with 70% identity, 100-bp matches, and thresholds below E−10 using METAIDBA. These filtered contigs were assembled and annotated using blastN against the NCBI nucleotide database. As a result, a microbial community structure with 1431 species was analyzed, among which Prevotella ruminicola 23 bacteria and Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus B316 were the dominant groups. In parallel, 201 sequences related with cellulase activities (EC.3.2.1.4) were obtained through blast searches using the enzyme.dat file provided by the NCBI database. After translating the nucleotide sequence into a protein sequence using Interproscan, 28 protein domains with cellulase activity were identified using the HMMER package with threshold E values below 10−5. Cellulase activity protein domain profiling showed that the major protein domains such as lipase GDSL, cellulase, and Glyco hydro 10 were present in bacterial species with strong cellulase activities. Furthermore, correlation plots clearly displayed the strong positive correlation between some protein domain groups, which was indicative of microbial adaption in the goat rumen based on feeding habits. This is the first metagenomic analysis of cellulase activity protein domains using bioinformatics from the goat rumen.