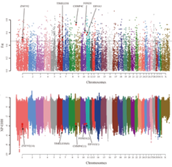
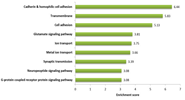
Previous studies of horse RNA-seq were performed by mapping sequence reads to the reference genome during transcriptome analysis. However in this study, we focused on two main ideas. First, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified by de novo–based analysis (DBA) in RNA-seq data from six Thoroughbreds before and after exercise, here-after referred to as “de novo unique differentially expressed genes” (DUDEG). Second, by integrating both conventional DEGs and genes identified as being selected for during domestication of Thoroughbred and Jeju pony from whole genome re-sequencing (WGS) data, we give a new concept to the definition of DEG. We identified 1, 034 and 567 DUDEGs in skeletal muscle and blood, respectively. DUDEGs in skeletal muscle were significantly related to exercise-induced stress biological process gene ontology (BP-GO) terms: ‘immune system process’; ‘response to stimulus’; and, ‘death’ and a KEGG pathways: ‘JAK-STAT signaling pathway’; ‘MAPK signaling pathway’; ‘regulation of actin cytoskeleton’; and, ‘p53 signaling pathway’. In addition, we found TIMELESS, EIF4A3 and ZNF592 in blood and CHMP4C and FOXO3 in skeletal muscle, to be in common between DUDEGs and selected genes identified by evolutionary statistics such as FST and Cross Population Extended Haplotype Homozygosity (XP-EHH). Moreover, in Thoroughbreds, three out of five genes (CHMP4C, EIF4A3 and FOXO3) related to exercise response showed relatively low nucleotide diversity compared to the Jeju pony. DUDEGs are not only conceptually new DEGs that cannot be attained from reference-based analysis (RBA) but also supports previous RBA results related to exercise in Thoroughbred. In summary, three exercise related genes which were selected for during domestication in the evolutionary history of Thoroughbred were identified as conceptually new DEGs in this study.
Previous studies of horse RNA-seq were performed by mapping sequence reads to the reference genome during transcriptome analysis. However in this study, we focused on two main ideas. First, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified by de novo–based analysis (DBA) in RNA-seq data from six Thoroughbreds before and after exercise, here-afte...
Previous studies of horse RNA-seq were performed by mapping sequence reads to the reference genome during transcriptome analysis. However in this study, we focused on two main ideas. First, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified by de novo–based analysis (DBA) in RNA-seq data from six Thoroughbreds before and after exercise, here-after referred to as “de novo unique differentially expressed genes” (DUDEG). Second, by integrating both conventional DEGs and genes identified as being selected for during domestication of Thoroughbred and Jeju pony from whole genome re-sequencing (WGS) data, we give a new concept to the definition of DEG. We identified 1, 034 and 567 DUDEGs in skeletal muscle and blood, respectively. DUDEGs in skeletal muscle were significantly related to exercise-induced stress biological process gene ontology (BP-GO) terms: ‘immune system process’; ‘response to stimulus’; and, ‘death’ and a KEGG pathways: ‘JAK-STAT signaling pathway’; ‘MAPK signaling pathway’; ‘regulation of actin cytoskeleton’; and, ‘p53 signaling pathway’. In addition, we found TIMELESS, EIF4A3 and ZNF592 in blood and CHMP4C and FOXO3 in skeletal muscle, to be in common between DUDEGs and selected genes identified by evolutionary statistics such as FST and Cross Population Extended Haplotype Homozygosity (XP-EHH). Moreover, in Thoroughbreds, three out of five genes (CHMP4C, EIF4A3 and FOXO3) related to exercise response showed relatively low nucleotide diversity compared to the Jeju pony. DUDEGs are not only conceptually new DEGs that cannot be attained from reference-based analysis (RBA) but also supports previous RBA results related to exercise in Thoroughbred. In summary, three exercise related genes which were selected for during domestication in the evolutionary history of Thoroughbred were identified as conceptually new DEGs in this study.